
Are you using data to identify prospects, harvest leads and nurture customers through the sales cycle? If not, you should. The right data can make a world of difference in business-to-business (B2B) sales. Rather than blindly reaching out to prospects, you can use a more methodical, data-driven approach. With that said, however, you should beware of the dangers of using bad data.
What is Bad Data?
Bad data can best be described as data that's outdated, incomplete and/or incorrect. This can happen for any number of reasons. Maybe the prospect entered his or her information incorrectly, or perhaps the prospect's contact information simply changed.
According to KISSMetrics, 40% of email users change their address at least once every two years. So, even if a prospect entered their correct address, it may have changed. Additionally, this same report indicates that 18% of all telephone numbers change at least once every year, and 20% of all postal addresses change annually. As you can see, bad data is a common occurrence that's nearly impossible to avoid.
How Bad Data Impacts B2B Marketing and Sales
To put the problem into perspective, a report by the Harvard Business Review (HBR) suggests that bad data costs U.S. businesses approximately $3.1 trillion -- yes trillion -- every year. When B2B companies are given bad data, it takes a toll on their productivity and efficiency. Rather than contacting prospects that may convert into customers, B2B salespersons reach a disconnected number or addresses. A single instance of bad data isn't going to have much of an impact, but if salespersons are constantly calling the wrong numbers and sending emails to the wrong addresses, it takes a heavy financial toll on the company.
Avoiding Bad Data
There are ways to avoid bad data, however. First and foremost, make sure you acquire your company's data from a reputable, reliable source. You can source data manually, or you can use a third-party service provider. When opting for the latter, make sure the service provider offers reliable, accurate data.
Additionally, you can mitigate the harmful effects of bad data by verifying and validating your data. Before reaching out to a prospect, for instance, you should check to ensure all of the appropriate fields are complete and contain the correct characters. If a prospect's phone number only has nine digits, for instance, you can assume it's bad and thus should be avoided.
What to learn more? Get in Touch
Latest Posts
-
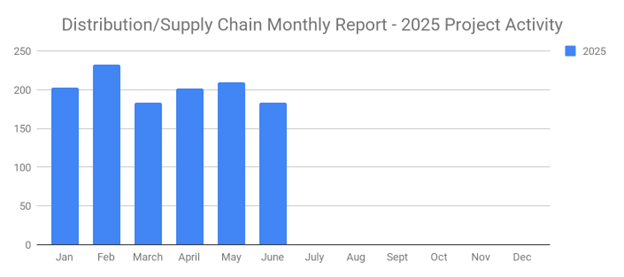
June's New Distribution and Supply Chain Planned Projects Return to March’s 183 Confirmed Figure
-
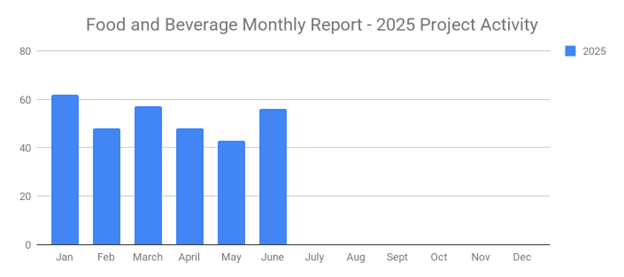
Food and Beverage Rebounds with 56 New Planned Projects Igniting Growth After Decline
-
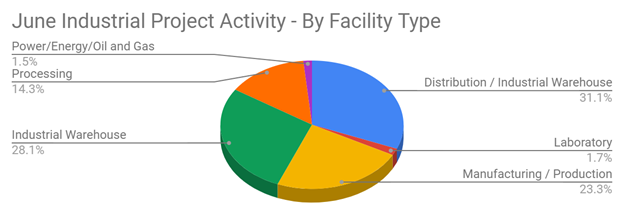
June 2025’s New Industrial Construction Projects Grew 7% Month-Over-Month
-
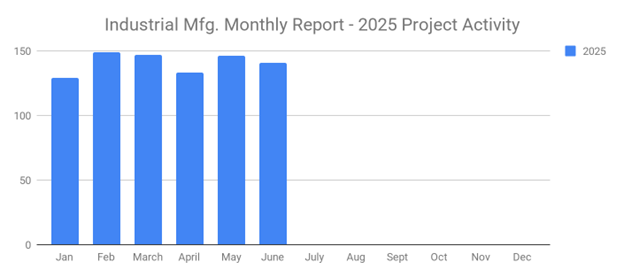
Q2 Industrial Manufacturing Soars 31% for Planned Projects Over $100M; June Planned Industrial Projects Hit 141

